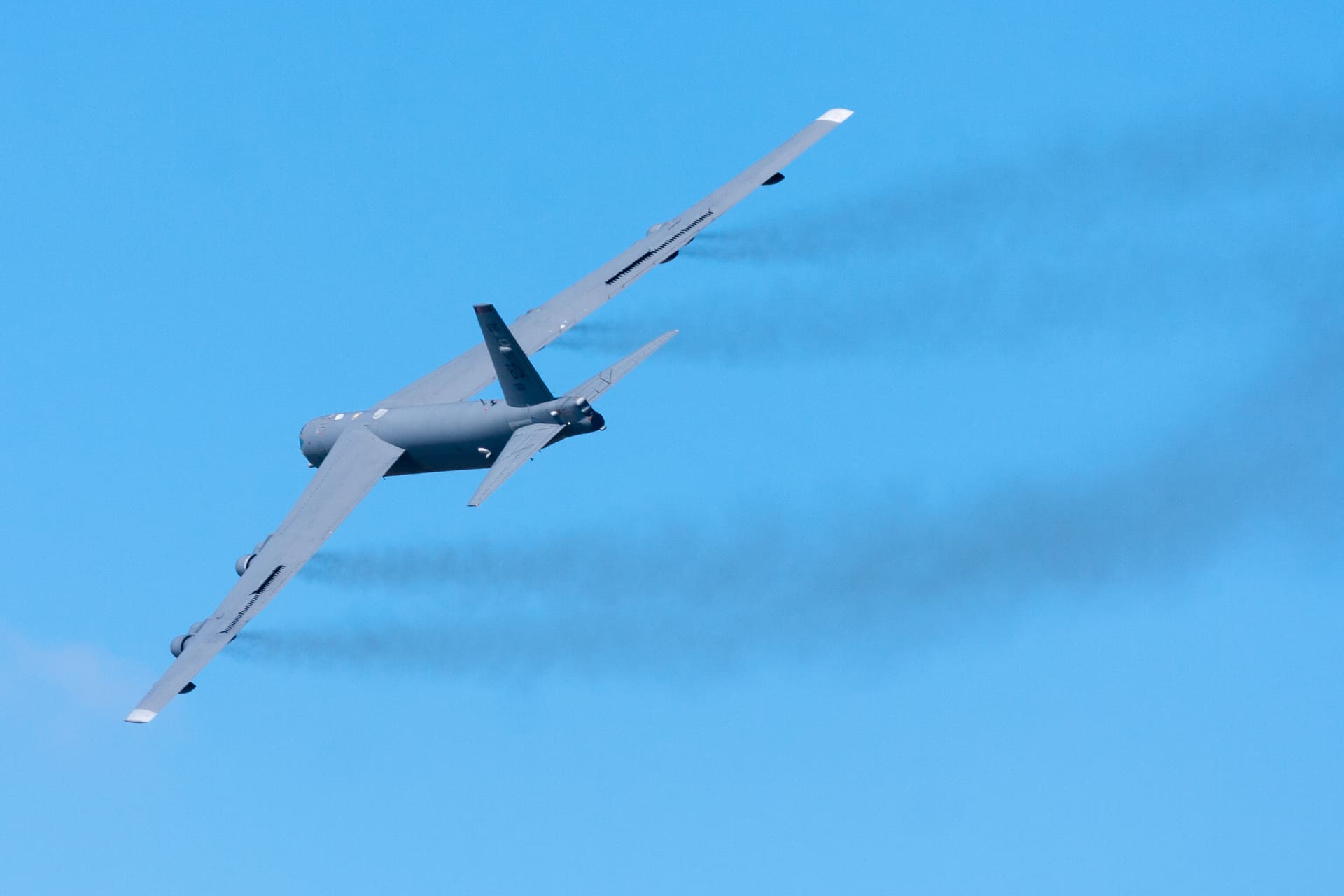
The B-52G Stratofortress was a variant of the iconic B-52 strategic bomber developed for the United States Air Force (USAF) during the Cold War era. Introduced in the early 1960s, the B-52G featured several improvements over earlier models, including more powerful engines and advanced avionics systems. With a maximum takeoff weight of over 220,000 pounds and a range exceeding 8,000 miles, the B-52G was capable of carrying a wide array of weapons, including nuclear bombs and cruise missiles. The B-52G played a significant role in the strategic deterrence mission of the USAF during the Cold War, participating in numerous training exercises and standing ready to respond to any potential threat. The aircraft was eventually retired from service in the early 1990s, as newer bombers entered the USAF inventory, marking the end of an era for this legendary aircraft.
General characteristics
- Crew: 5 (pilot, co-pilot, radar navigator, navigator, electronic warfare officer)
- Length: 48.5 m (159.33 ft)
- Wingspan: 56.4 m (185 ft)
- Height: 12.4 m (40.66 ft)
- Empty weight: 83,250 kg (183,750 lb)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 220,000 kg (488,000 lb)
- Powerplant: 8 × Pratt & Whitney TF33-P-3/103 turbofan engines, 76.5 kN (17,200 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,047 km/h (580 knots) at 10,000 ft (3,050 m) altitude
- Cruise speed: 912 km/h (492 knots)
- Range: 14,080 km (7,610 nmi) with 20,000 kg (44,000 lb) of bombs
- Service ceiling: 15,000 m (50,000 ft)
Armament
- Guns: 1 × 20 mm (0.787 in) M61 Vulcan cannon in a remote-controlled tail turret
- Bombs: Up to 31,500 kg (69,750 lb) of ordnance, including conventional or nuclear bombs, mines, and missiles